
The results of the FOCUSDEM program and CLEANDEM project mark a pivotal shift in optimizing the D&D operations essential to the life cycles of nuclear facilities, whether aging or newly planned. The FOCUSDEM-funded PhD theses, supported by CEAList, addressed three major challenges in the radiological characterization of decommissioning sites—a cornerstone of operational safety.
Andréa Macario Barros’ research focused on a modular system for radiological mapping. This system automates sensor localization with SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) technology, enabling more precise data acquisition and significantly reducing human error. This breakthrough is vital for reliably mapping contaminated areas, a key priority for field operators.
Dilan Tüzün’s research, building on pioneering work by the LNHB (Laboratoire National Henri Becquerel), developed moldable or deformable radioactive sources tailored to the diverse surfaces and materials encountered in the field, improving instrument calibration accuracy.
Aya Kanj’s research advanced a portable neutron spectro-imager designed to identify neutron radiation sources. This system complements gamma imagers and proves particularly valuable in environments with shielding that blocks gamma detection.
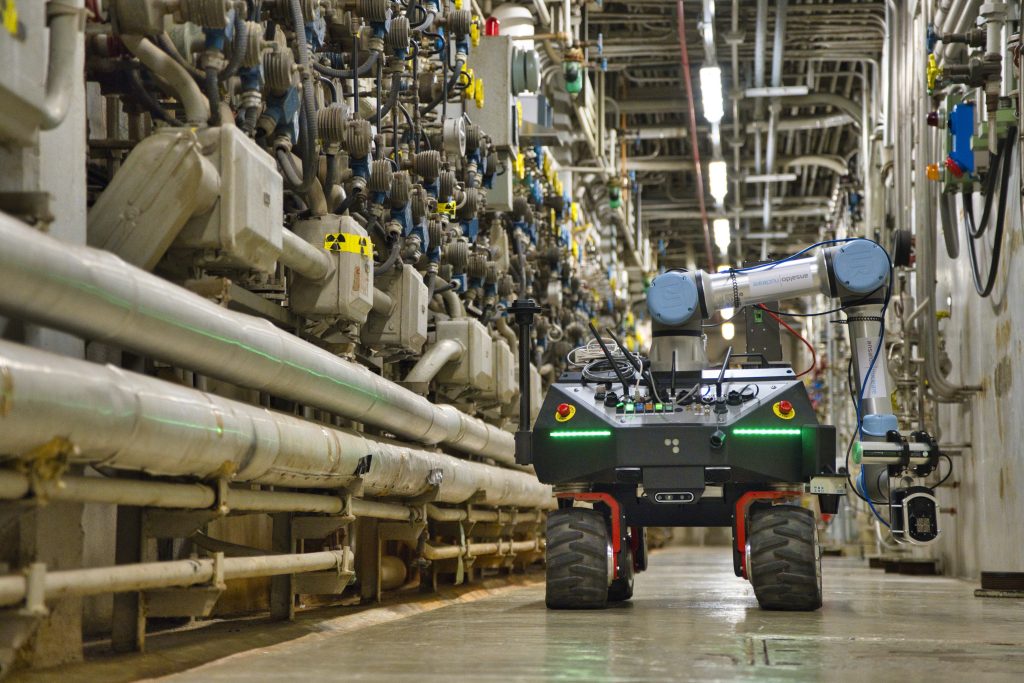
In parallel, the European CLEANDEM project—dedicated to robotic measurement technologies for D&D—concluded with real-world demonstrations of three CEA-List innovations deployed on an autonomous robot:

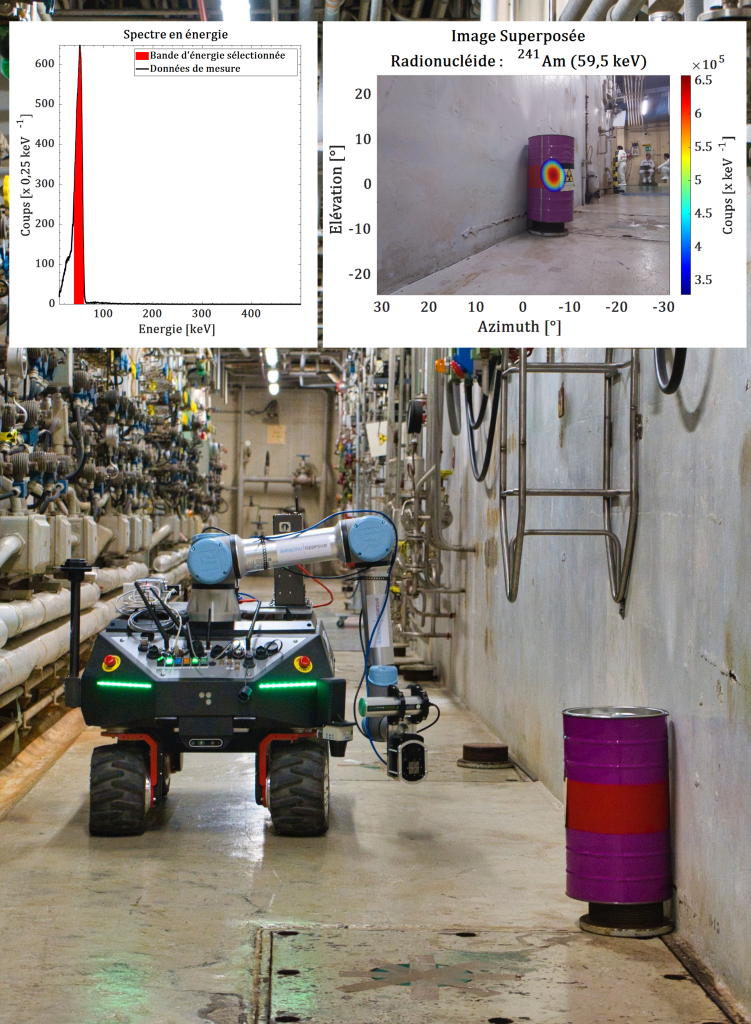
These advances underscore CEA-List’s commitment to addressing nuclear decommissioning challenges—a field where safety, precision, and technological innovation are more crucial than ever. They reduce worker exposure, enhance measurement accuracy, and streamline site management. They also enable greater automation, making processes more efficient and less hazardous for personnel.
By delivering reliable radiological data, these technologies also pave the way for crisis management, accelerating information gathering. In the case of autonomous drones and robots, they can free first responders to focus on their primary tasks while an autonomous fleet collects data to avoid exposing them to radiological hazards.
This work is part of ongoing R&D efforts, including CEA’s participation in the European project XS-ABILITY, which aims to enhance and miniaturize Nanopix3 and a neutron/gamma measurement system for improved characterization of nuclear decommissioning sites—particularly by deploying them on drones and autonomous robots.
These breakthrough innovations will improve detection, mapping, and identification of radioactive sources in D&D operations.
The system is also able to provide a digital model of the studied area, enriched with the radiological information provided by the sensors, allowing creation of a digital twin.