
AI is making increasing inroads into the systems we use every day. But AI deployment in critical systems, where there is no room for even the smallest malfunction, will be the true marker of the technology’s success. With potential costs that include not only economic losses, but also irreparable harm to people and the environment, the need for software certification is pressing. Put simply, users need to know that software will behave as specified in nominal operating conditions.
CEA-List researchers are developing formal verification tools for software containing artificial intelligence. Formal verification provides robust mathematical proof of how an AI works. This assurance is vital to deploying AI in industrial and other operational environments. Our PyRAT formal neural network verification tool was created in 2019 for precisely this purpose.
PyRAT can formally verify the stability of a neural network whose inputs are exposed to minor disruptions. In automotive computer vision systems, for instance, PyRAT can verify that a neural network in charge of recognizing road signs will still work as intended in rain or low light.
PyRAT can also verify that a neural network respects certain requirements in its specifications (as long as the requirements can be expressed using mathematical formulae).
This type of verification is notoriously complex. PyRAT uses conventional abstract interpretation methods plus software optimizations (GPU parallelization, matrix operations, etc.) specific to neural networks. PyRAT also features an accurate representation of complex neural network operations. This reduces abstraction errors during analysis. And, thanks to an iterative “divide and conquer” approach and new optimization methods, PyRAT has become much faster and more accurate in just a year.
PyRAT has been used in the VNN-Comp, the international neural network verification competition, for two years running, coming in third in 2023 and second in 2024. The wins mark the research community’s recognition of PyRAT as a top-tier tool—already deployed in industrial use cases—and reinforce CEA-List’s position as a leader in formal verification.
What is next for PyRAT? We plan to continue to improve the tool’s performance and expand into new, more complex types of neural networks (recurrent, transformer, etc.). Finally, adaptations will be made to PyRAT so that it can be used for embedded (quantized) neural networks.
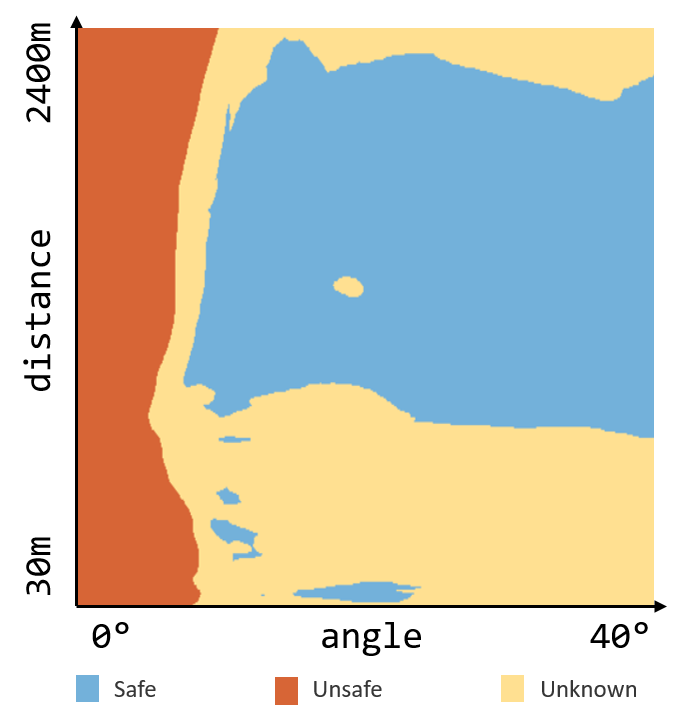
Our second-place win at VNN-Comp is validation that PyRAT is effective at ensuring the safety and security of AI-based systems.
Safety assessment of an anomaly detection neural network for offshore drilling platforms
Image-based weld robustness assessment on an automotive manufacturing line
Safety of embedded neural network for drone collision avoidance