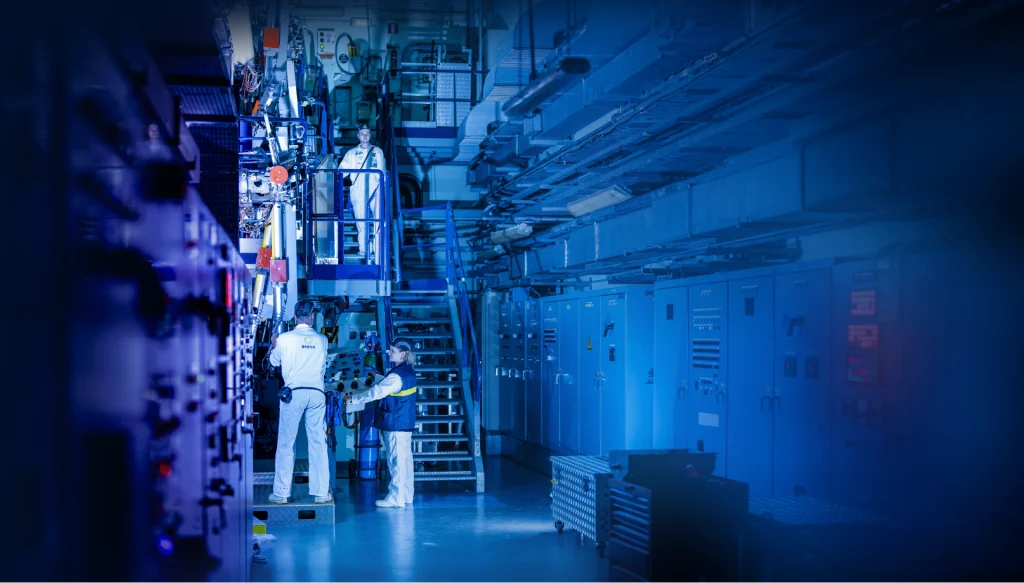

Nuclear specialist Orano’s Udd@Orano project was created to bring the company’s industrial facilities into the future. It was also one of several projects selected for France’s national nuclear-industry support program, which kicked off in December 2021 as part of the nation’s France Relance 2030 economic revitalization plan. Udd@Orano aligns with France’s commitment to modernizing nuclear fuel cycle facilities to buttress the nation’s energy sovereignty. The purpose of the project, which ran from 2022 to 2024, was to develop new technologies to improve fuel cycle facility performance and operator safety at Orano.
One of twelve project partners, CEA-List contributed know-how in instrumentation, simulation, and artificial intelligence (AI), mobilizing 30 research engineers from six laboratories* to develop eleven prototype measurement systems plus software to meet Orano’s real-world operational needs.
* Five CEA-List laboratories and one laboratory from the CEA Institute for Research on the Fundamental Laws of the Universe.
CEA-List designed and tested a set of miniaturized, portable, high-performance detection systems that deliver comprehensive radiological measurements of the environment. The goal is to ensure that operators can carry out their job tasks safely.
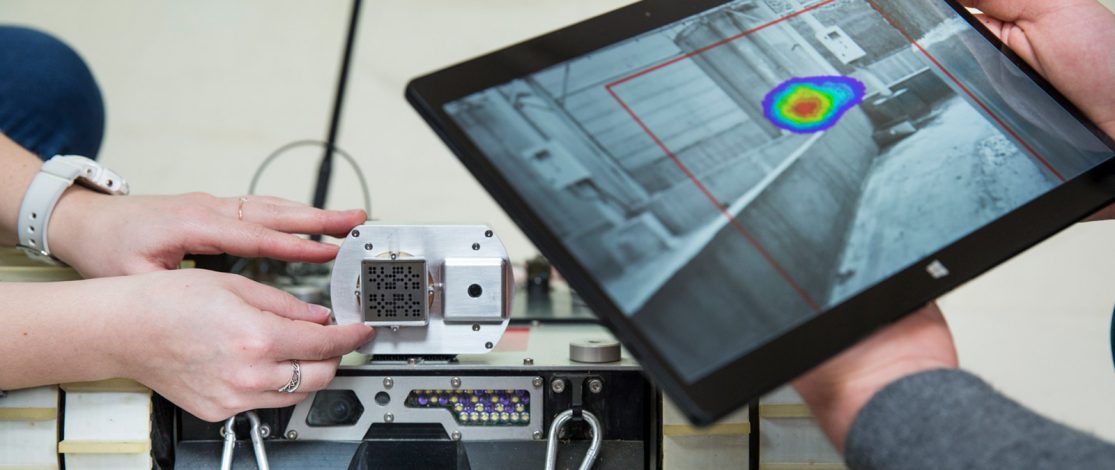
Credit: Cyrille Dupont / The Pulses
CEA-List also developed additional technologies, like a radiation-resistant multi-core optical fiber for multi-point, long-distance dose measurement in highly irradiating environments that are tough to access. Last, but not least is CEA-List’s innovative software, IA-MCA, designed to address complex operating issues. Combining spectral analysis, AI, and simulation, the software uses inference from spectrometry measurements to produce generative models that can be used to estimate unknown parameters and uncertainties. IA-MCA eliminates manual trial-and-error in the assessment of radiological activity, saving precious time.
The prototypes developed by CEA-List are expected to be field tested at Orano’s plant in La Hague, France in 2025. IA-MCA software has already been rolled out at Orano. Nuclear detection specialist Radeo will also be including the software in its lineup.
Additional CEA-List technologies developed as part of this project are currently in the process of being transferred to industrial partners.
This project gave us an opportunity to showcase our ability to understand our partners’ operational needs and our flexibility in aligning our developments with those needs. The Udd@Orano project also pushed us to be creative, gave our instrumentation developments renewed energy, and produced some interesting opportunities for the future.