
At CEA-List, we are investigating ways to leverage the enhanced privacy of near-memory computing architectures for data encryption. A computational SRAM (C-SRAM) IP was implemented and integrated into a SoC on an ASIC (the VASCO-2 circuit; see Figure 1). The circuit, with its 32-bit RISC-V core, memory, and C-SRAM accelerator, integrates both computing and memory.
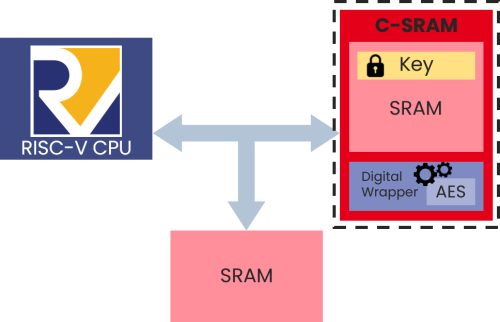
The C-SRAM’s near-memory computing capabilities were used to port the AES encryption algorithm. This circuit, with its hardware accelerator, is comparable to a software-only version running on the RISC-V core. The C-SRAM also has an embedded PUF encryption key generator.
In 2022 an ASIC was fabricated on GlobalFoundries’ 22 nm FD-SOI platform. A purpose-built test board with separate power supply gates for the matrix, peripheral, and logic components of the C-SRAM enabled verification of the IP’s proper functioning and characterization of the substrate.
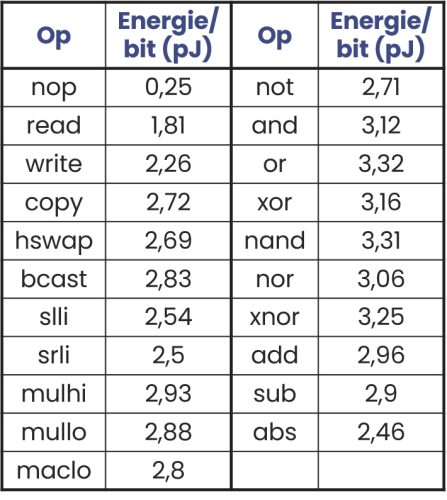
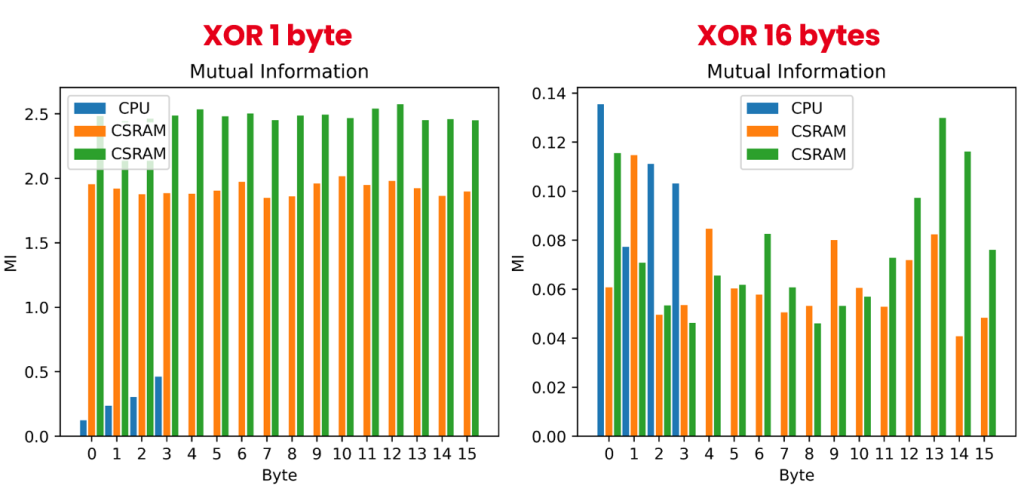
C-SRAM’s parallelism can be exploited to effectively reduce architecture-related leakage during data transfer, a topic that will be investigated experimentally in upcoming research.
The technology in use:
Major projects:
This ambitious project leveraged hardware and software cybersecurity innovations developed by several CEA labs. We were able to characterize and demonstrate the technologies on an ASIC target