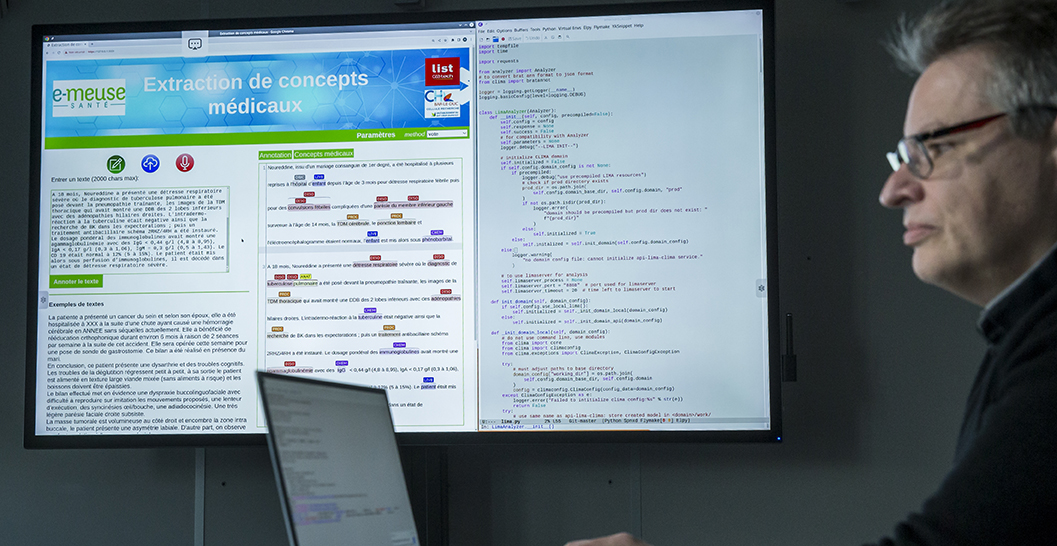
Today’s medical coding systems do structure some patient data, but not the textual data contained in speech therapy reports and notes. Automated report writing processes can help identify certain patient profiles more rapidly. And the ability to explore the content of medical and paramedical records could provide new insights that can help advance clinical practice and improve the quality of care. The objective of this research is to develop a method to automatically identify unstructured textual data in medical records so that relevant lexical units can be extracted to meet the needs of healthcare professionals.
The project could help with practical problems like answering questions about the feasibility of a clinical study or exploring clinical practices that are sufficiently represented within a given perimeter to explore variables and establish evidence-based protocols. These capabilities will also make risk/benefit analyses easier. How care is delivered can be documented and the care pathway and any complications assessed.
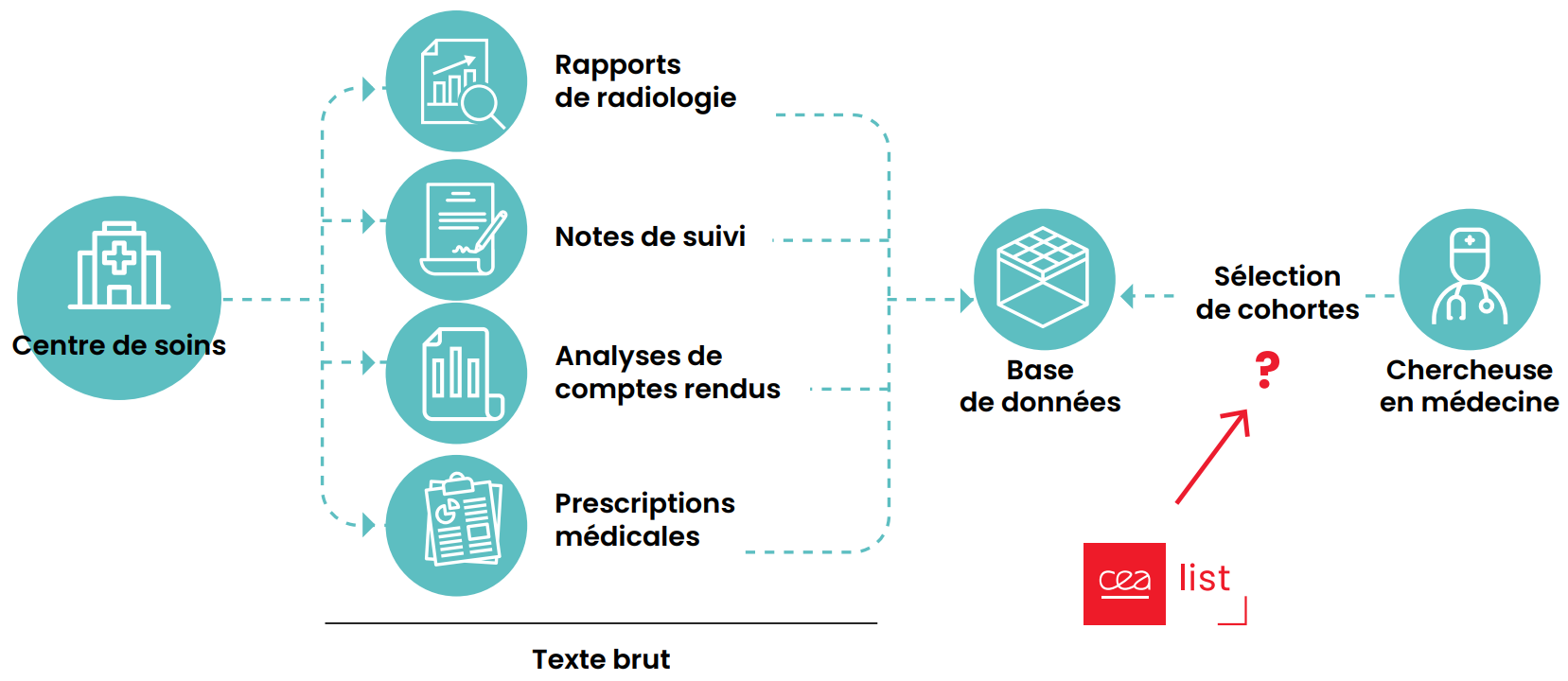
For clinical studies, the method could help determine things like how many stroke patients have speech apraxia. For clinical practice, it could help search for how to insert a nasogatric tube in cases of post-stroke neurological dysphagia in order to improve procedures, for example.
The automated processing is accessed through a search
engine, with:
The tool will help healthcare professionals structure the information available to them, improve their knowledge of a particular issue, and get a quick overview of a patient’s medical history, for example.
Speech and language pathology, at the intersection of the biomedical and social sciences, focuses on conditions affecting language, communication, and swallowing. This kind of research partnership enables a more critical perspective and high-level epistemic thinking.