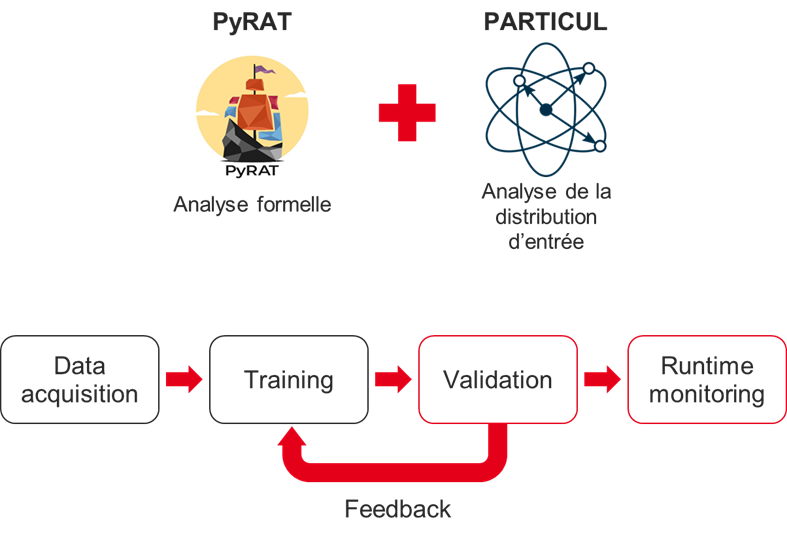
As artificial intelligence (AI) has improved, systems based on the technology have seen their popularity skyrocket. The PyRAT and PARTICUL tools developed by CEA-List enable detection and protection against adversarial attacks.
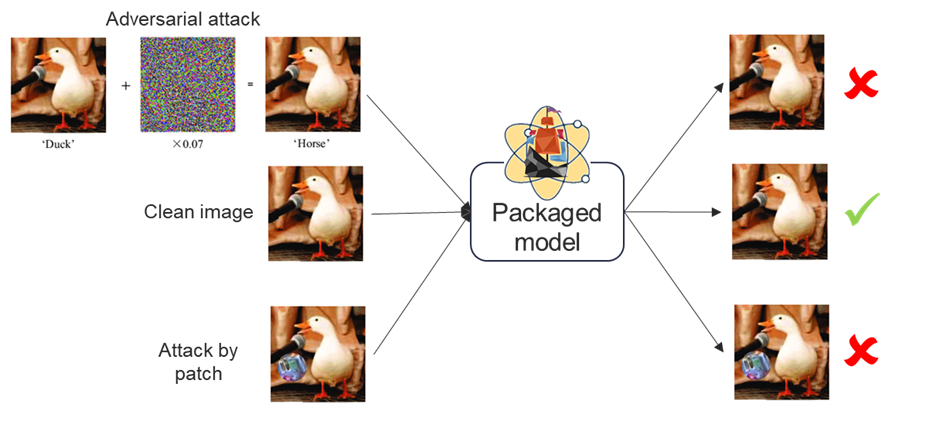
AI is now a key component in growing numbers of consumer and business solutions, making it a part of our daily lives. Like all information systems, AI systems are vulnerable to a variety of attacks throughout the development cycle, from data acquisition to training to implementation. It is well-known that AI systems are fragile when faced with attacks: As early as 2014 researchers demonstrated that an AI’s output could be altered by disturbances—invisible to the naked eye—introduced into the images input into the system. Patch attacks operate along the same lines: Adversarial pixels are injected into an image next to an object of interest, altering how the AI recognizes the object.
CEA-List combined its PyRAT and PARTICUL tools in a new solution designed to fend off these attacks. PyRAT, a formal neural network verification tool, leverages abstract interpretation, providing strong mathematical guarantees of the security of an AI model. PARTICUL is used to build detectors of recurrent parts in a data set and assign a confidence score as to whether these parts are in the model inputs. When combined during AI system validation and monitoring, these tools help detect and fend off adversarial attacks once the AI system has been deployed.